This is a series of readings from and notes and commentary upon
Augustine of Hippo’s Harmony of the Evangelists.
In this episode we are looking at Book 2, chapter 3-4 where
Augustine addresses both supposed conflicts between and among the genealogies
of Matthew 1 and Luke 3.
2.3: A statement of the reason why Matthew enumerates one
succession of ancestors for Christ, and Luke another.
Augustine begins by noting in particular a difference between
Matthew and Luke in the line between David and Joseph in the two genealogies. They
follow different directions with Matthew offering a series “beginning with
David and traveling downwards to Joseph,” and Luke, on the other hand, having “a
different succession, ”tracing it from Joseph upwards….” The main source of the
difference, however, is in the order between Joseph and David and the fact that
Joseph is listed as having two different fathers. Augustine explains that one
of these was Joseph’s natural father by whom he was physically begotten (Jacob,
in Matthew), and the other was his adopted father (Heli, in Luke). Both of
these lines led to David.
Augustine further notes that adoption was an ancient custom. Though
terms like “to beget” generally indicate natural fatherhood, Augustine notes
that natural terms can also be used metaphorically, so Christians can speak of
being begotten by God (e.g., cf. John 1:12-13: “to them he gave power to become
the sons of God”). Augustine thus concludes, “It would be no departure from the
truth, therefore, even had Luke said that Joseph was begotten by the person by
whom he was really adopted.” Nevertheless, he sees significance in the fact
that Matthew says “Jacob begat Joseph” (Matthew 1:16; indicating he was the
natural father) and Luke says, “Joseph, which was the son of Heli” (Luke 3:23;
indicating he was the adopted father of Joseph). Those unwilling to seek
harmonizing explanations of such texts “prefer contention to consideration.”
2.4: Of the reason why forty generations (not including
Christ Himself) are found in Matthew, although he divides them into three
successions of fourteen each.
Augustine begins by noting that consideration of this matter
requires a reader “of the greatest attention and carefulness.” Matthew who
stresses the kingly character of Christ lists forty names in his genealogy. The
number forty is of obvious spiritual significance in the Bible. Moses and
Elijah each fasted for forty days, as did Christ himself in his temptation. After
his resurrection, Christ also appeared to his disciples for forty days. He sees
numerological significance in the fact that forty is four time ten. There are
four directions (North, South, East, and West) and ten is the sum of the first
four numbers.
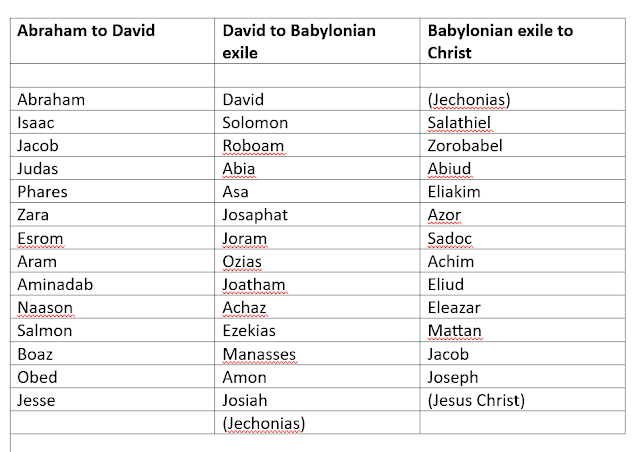
Matthew intentionally desires to list forty generations, but
he also suggests three successive eras (Abraham to David; David to Babylonian
exile; Babylonian exile to Christ). This would be fourteen generations each for
a total of forty-two, but Matthew, Augustine suggests, offers a double
enumeration of Jechonias, making it “a kind of corner” and excluding it from
the overall count, resulting then in the more spiritually significant number
forty.
Augustine suggests that Matthew’s genealogy stresses Christ
taking our sins upon himself, while Luke, who focuses on Christ as a Priest, stresses
“the abolition of our sins.” He sees significance in Matthew’s line from David
through Solomon by Bathsheba, acknowledging David’s sin, while Luke’s line
flows from David through Nathan, whom Augustine erroneously ties to the prophet
Nathan, by whose confrontation with David, God took away sin.
He also sees numerological significance in the fact that Luke’s
genealogy includes seventy-seven persons (counting Christ and God himself). He
sees the number seventy-seven as referring to “the purging of all sin.” Eleven
breaks the perfect number ten, and it was the number of curtains of haircloth
in the temple (Exodus 26:7). Seven is the number of days in the week. Seventy-seven
is the product of eleven times seven, and so it is “the sign of sin in its
totality.”
Conclusion:
The harmonization
of the genealogies has been a perennial issue in Gospel studies from the
earliest days of Christianity (see Eusebius’ citation of Africanus in his EH).
Augustine maintains the continuity and unity of both Gospel genealogies while
also noting the uniqueness of each individual Gospel account. In both
genealogies Augustine offers pre-critical insight into the intentional use of spiritually
significant numbers (forty in Matthew; seventy-seven in Luke) to heighten what
he sees as the theological perspectives and intentions of the Evangelists.
JTR
Addendum:
Here's a chart showing Augustine's breakdown of the genealogy in Matt 1:1-17 which yields 40 names according to his calculation. He excludes in his scheme Jechonias as "a kind of corner" and Jesus Christ as "the kingly president" over the whole.

No comments:
Post a Comment